Summary: Six Sigma Method, employed for quality management, utilizes various tools and techniques to enhance business processes and achieve high-quality results. By aiming to minimize variations and defects and targeting a goal of 3.4 defects per million opportunities, organizations can streamline operations, boost quality control, and optimize project management. Furthermore, this approach often combines principles with certifications such as Green Belt and Black Belt, indicating proficiency in Six Sigma practices. Across industries, the Six Sigma Method drives ongoing enhancements and ensures favorable business results by utilizing its principles and tools.
The Origins of Six Sigma Method
Originally developed by Motorola in the 1980s to address the need for enhancing quality in manufacturing processes Six Sigma gained traction through General Electric (GE) under Jack Welch’s leadership during the 1990s. Since then numerous organizations in sectors such, as manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and services have embraced Six Sigma widely.
Advantages of Implementing Six Sigma
The implementation of Six Sigma brings advantages to organizations including enhancing operational efficiency reducing errors and defects elevating customer satisfaction levels boosting profitability and fostering a culture of continuous enhancement. By embracing the Six Sigma methodology companies can achieve outcomes enhance efficiency and secure a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Get Acquaint with the Six Sigma Approach
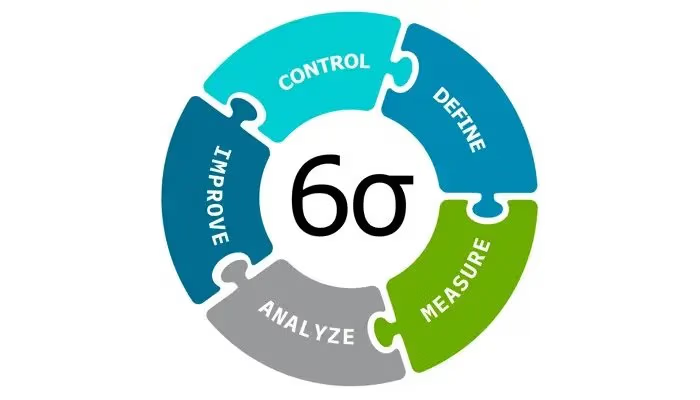
The Six Sigma methodology offers a problem-solving and process enhancement strategy utilizing both DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design Verify) methodologies. It serves as a framework, for enhancing business processes by emphasizing Six Sigma principles and Sigma levels to attain top-notch quality. Lean Six Sigma merges concepts to streamline processes and minimize inefficiencies. The goal of Six Sigma is to reach three Sigma from the average or within Six Sigma levels for quality and productivity. Obtaining green and black belt certifications is crucial for individuals aspiring to become experts in Six Sigma who lead initiatives and implementations within companies. It leverages techniques and tools geared towards enhancing businesses and supporting Six Sigma projects and implementations. In today’s world, Six Sigma serves as a methodology, for achieving significant breakthroughs and advancements.
The DMAIC Method
When seeking to enhance processes that fail to meet desired performance levels, the DMAIC method is employ. DMAIC, which is an acronym for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, provides a structured approach. First followed by measurement of key parameters. Then, an analysis is conducted to identify root causes of inefficiencies. Subsequently, improvements are implements based on the analysis. Finally, control measures are established to sustain the improvements. By utilizing the DMAIC method, organizations can systematically address process deficiencies and drive continuous improvement. The acronym stands for;
Define Phase
At this stage, project objectives are clearly outlined. The problem statement and key metrics, for measuring success are established. A project team is. The project’s scope is defined.
Measure Phase
This phase centers on comprehending the state of the process. Data is. Analyzed to determine performance and pinpoint areas for enhancement.
Analyze Phase
Data collected in the phase undergoes analysis to pinpoint the root causes of defects and errors. Statistical analysis tools, like cause and effect diagrams and Pareto charts. It is use to identify the factors impacting process performance.
Improve Phase
The improvement phase focuses on devising and executing solutions to tackle identified root causes. Potential solutions are assessed experiments may be conducted to test proposed changes’ effectiveness the optimal solution is chosen and implemented leading to process optimization.
Control Phase
This phase concentrates on upholding improvements realized in preceding phases.
Control plans are created to oversee and manage the performance of a process. Statistical process control (SPC) methods can be utilized to ensure that the process remains stable and meets the desired performance standards.
The DMADV Methodology
The DMADV methodology is employed when aiming to develop products or processes that satisfy customer requirements with a probability of success. It consists of;
Define Phase
The DMAIC approach entails the define phase, while in DMADV, the define phase serves to establish project objectives, identify the issue or opportunity, and outline the project scope. However, in contrast to DMAIC, DMADV places greater emphasis on the design of a process or product rather than the enhancement of an existing one.
Measure Phase
In this phase, customer requirements are translates thoroughly into specifications. Additionally, research on benchmarking and best practices may be conducted to gather insights on processes or products in industries.
Analyze Phase
During the analysis phase, the evaluation of design options takes place, leading to the selection of the most suitable one. Multiple concepts and alternatives are explored while taking into account trade-offs. Furthermore, testing through simulation and prototyping may be conducted to validate the design. Additionally, an assessment of risks and potential failure modes is performed.
Improve Phase
Transitioning to the verification phase, this particular stage of DMADV focuses on validating and confirming the design prior to full-scale implementation.
Control Phase
The decision between DMAIC and DMADV depends on the nature of the project and the desired outcomes.
Is your process optimization reaching its full potential?
Manufacturing Operations Management Software (MOM) provides real-time data and process control for continuous improvement.
Variations in Six Sigma Methodologies
Six Sigma methodologies can be customized based on expertise levels and specific business requirements. Some common types include;
Lean Six Sigma
By combining Lean Sigma principles with Lean Manufacturing tools, Lean Six Sigma aims to achieve waste elimination and process flow enhancement. Furthermore, its primary objective is to drive efficiency improvements while consistently prioritizing customer value. Notably, this methodology emphasizes the significance of pinpointing areas for improvement, removing unnecessary tasks, streamlining operations, and ultimately reducing turnaround times. As part of a broader set of lean management methods, Lean Six Sigma ensures that organizations adopt a structured approach to operational excellence while maintaining a strong focus on quality and efficiency.
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
DFSS centers on a meticulous process of grasping customer requirements and effectively translating them into precise design specifications. Furthermore, it utilizes an array of powerful tools such as Quality Function Deployment (QFD), Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), and Design of Experiments (DOE) to meticulously ensure that the design seamlessly aligns with the intended performance goals. By leveraging these tools, DFSS enables organizations to proactively address potential issues, optimize designs, and deliver exceptional outcomes that truly resonate with the customers.
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
A Lean Six Sigma Green Belt refers to an individual who has undergone training and certification in Lean Six Sigma methodologies. These Green Belts effectively contribute to process enhancement projects, typically serving as valuable team members under the guidance and supervision of experienced Black Belts or Master Black Belts. With their specialized knowledge, Green Belts actively engage in data gathering, analysis, and the execution of improvement efforts. By employing their expertise, they play a pivotal role in identifying areas for enhancement and implementing targeted strategies to drive positive change within the organization.
Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
A Lean Six Sigma Black Belt represents an individual who has achieved a high level of expertise in Lean Six Sigma practices. These skilled professionals not only possess deep knowledge but also take on leadership roles within projects, serving as catalysts for change. Through their guidance and expertise, they play a pivotal role in driving organizational transformation and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
These highly accomplished professionals, referred to as Master Black Belts, possess an extensive wealth of knowledge and experience in guiding and mentoring Lean Six Sigma practitioners. With a comprehensive understanding of the intricacies involved, they play a pivotal role in overseeing projects, providing guidance to both Green Belts and Black Belts, and driving initiatives aimed at fostering continuous improvement within the organization. Through their leadership and mentorship, Master Black Belts effectively cultivate a culture of excellence and ensure the successful implementation of Lean Six Sigma principles.
Six Sigma Certification and Training
Certification in Six Sigma holds significant importance as it effectively showcases an individual’s competence in applying Six Sigma methodologies to enhance processes. Moreover, being certified not only enhances credibility and recognition within the organization but also elevates one’s standing in the highly competitive job market. By obtaining certification, professionals demonstrate their unwavering dedication to maintaining quality standards and continually improving practices. Consequently, employers frequently seek out certified professionals to ensure the successful execution of Six Sigma projects, recognizing the value they bring to the table.
Within the realm of Six Sigma certification various levels exist, each signifying levels of proficiency and responsibilities;
Yellow Belt
Individuals who hold a Yellow Belt certification demonstrate a solid understanding of Six Sigma principles and tools. By leveraging their knowledge and skills, Yellow Belts actively participate in collaborative efforts aimed at enhancing organizational processes. Their involvement strengthens the overall Six Sigma implementation and reinforces the collective pursuit of continuous improvement.
Green Belt
Under the guidance and supervision of Black Belts, they actively contribute towards the achievement of project objectives. Leveraging their expertise, Green Belts play a pivotal role in implementing targeted strategies and driving measurable improvements within the organization.
Six Sigma Black Belt
Equipped with exceptional skills and comprehensive knowledge, they have the capability to lead and oversee process improvement projects independently. Their pivotal role involves not only instigating change but also attaining significant enhancements in performance. Through their proficient leadership, they spearhead initiatives that foster continuous improvement and propel the organization towards higher levels of excellence.
Six Sigma Master Black Belt
Master Black Belts, as seasoned professionals with extensive expertise, assume a crucial role in providing direction, support, and mentoring to both Green Belts and Black Belts. They effectively contribute to the widespread implementation of Six Sigma methodologies throughout the entire organization. Furthermore, at an advanced level, Master Black Belts actively foster a culture of continuous improvement, driving initiatives aimed at achieving excellence.
Selecting the Appropriate Certification Program
When making a decision about a Six Sigma certification program, it is crucial to carefully consider the following factors:
- Curriculum; Evaluate the curriculum to ensure it comprehensively covers the concepts, methodologies, and tools of Six Sigma at the certification level desired.
- Instructor Credentials; Assess the qualifications and experience of the training instructors carefully.
- Support and Additional Resources; It's important to check whether the certification program offers support like study materials, practice tests, and access to a community of professionals, for guidance and learning.
- Cost and Time Investment; Take into account the cost of the certification program as the time needed to complete it. Make sure it fits your budget and schedule to meet your needs.
Key Principles of Six Sigma
To effectively apply Six Sigma methodologies it is crucial to grasp and adopt the core principles that serve as the foundation of this approach. These guiding principles inform decision-making processes. Promote a data-driven customer-focused strategy, for enhancing processes. The core tenets of Six Sigma include;
1. Data-Driven Decision Making
Six Sigma heavily relies on data and statistical analysis to steer decision-making processes. Decisions are made based on evidence rather than assumptions or personal opinions. Data is gathered, analyzed, and utilized to pinpoint root causes evaluate process performance, and validate the success of improvement endeavors.
2. Emphasis on Meeting Customer Needs
Customer satisfaction lies at the heart of Six Sigma practices. The desires, expectations, and demands of customers are. Given priority. Efforts to enhance processes are geared towards meeting or exceeding customer expectations providing value and fostering customer loyalty.
3. Continuous Process Improvement and Reduction in Variability
The primary goal of Six Sigma is the enhancement of processes by eradicating defects, errors, and inefficiencies. It strives to process variability to ensure predictable results. By identifying and rectifying the causes of variation organizations can enhance process capability levels significantly. Deliver products/services with minimal defects.
4. Utilization of Statistical Tools and Techniques
Analysis plays a crucial role in the implementation of Six Sigma methodologies. Various methods and tools, such as hypothesis testing, regression analysis, control charts. The experimental design, are employed to thoroughly examine data, identify patterns and trends, validate improvement projects. That make data-driven decisions. By utilizing these tools, organizations can actively engage in data analysis, enabling them to derive meaningful insights and take appropriate actions. This analytical approach enhances the effectiveness of Six Sigma methodologies and enables organizations to drive continuous improvement and achieve desired outcomes.
5. Teamwork Across Functions
In the Six Sigma Method, there is an emphasis on collaboration and cooperation among departments and levels within an organization. Improvement endeavors often involve individuals from areas working together towards objectives. This cross-functional collaboration fosters a variety of viewpoints and expertise resulting in solutions and improved organizational cohesion.
6. Support from Leadership and Management
The support of leadership is vital for the implementation of the Six Sigma Method. Senior leaders allocate resources to foster a culture of enhancement and actively engage in improvement projects. They outline the vision emphasize the significance of Six Sigma initiatives and ensure alignment with objectives. Support from management at all levels is crucial for instigating change and maintaining improvement efforts.
By embracing these core principles businesses can cultivate an environment of enhancement leading to improvements in quality standards, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction levels, and overall profitability.
FAQ | Six Sigma Method
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma Method is a data-driven approach to process improvement that aims to reduce defects and variations in business processes. It focuses on achieving high levels of quality and efficiency by identifying and eliminating the root causes of problems.
What are the key principles of Six Sigma?
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Decisions are based on statistical analysis, not assumptions.
- Customer Focus: Processes are optimized to meet customer needs and expectations.
- Process Improvement & Variation Reduction: Eliminating defects and inconsistencies ensures efficiency.
- Use of Statistical Tools: Methods like control charts and regression analysis identify improvement areas.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Teams across departments work together to enhance processes.
- Leadership Support: Strong management commitment drives Six Sigma success.
How does Six Sigma compare to other improvement methodologies?
Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and process variability through data-driven analysis, while other methodologies, like Lean and Kaizen, emphasize efficiency and continuous improvement. Understanding Kaizen meaning is essential, as it promotes small, incremental changes driven by employees, whereas Six Sigma follows a structured approach like DMAIC to achieve measurable process optimization. Many organizations combine these methods to maximize efficiency and quality.
Why is Six Sigma certification worth it?
Six Sigma certification demonstrates your proficiency in process improvement methodologies and enhances your career prospects. It validates your ability to lead and contribute to successful improvement projects, and organizations often prefer certified professionals for critical roles.
What are the different Six Sigma certification levels?
There are several levels of Six Sigma certification, including Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, and Master Black Belt. Each level represents a different level of expertise and responsibility in implementing Six Sigma methodologies.
Green Belt vs. Black Belt - What’s the difference?
A Green Belt has a comprehensive understanding of Six Sigma methodologies and tools and can lead process improvement projects under the guidance of a Black Belt. A Black Belt is an expert who can independently lead and manage complex improvement projects and drive organizational change.
What does a Master Black Belt do?
A Master Black Belt is the highest level of Six Sigma expertise. They provide leadership, guidance, and mentoring to Green and Black Belts. Master Black Belts oversee multiple projects and drive strategic initiatives to promote continuous organizational improvement.
How do I choose the right Six Sigma certification program?
When choosing a Six Sigma certification program, consider factors such as accreditation, curriculum, delivery method, instructor qualifications, support and resources, cost, and time commitment. Research and compare multiple programs to find the one that aligns with your needs and career goals.
Image: Adobe Stock – Copyright: © j-mel – stock.adobe.com