Summary: Continuous improvement is a powerful approach that enables organizations to adapt, evolve, and thrive in an ever-changing business landscape. By embracing a mindset of continuous learning, organizations can continually enhance their processes, products, and services, driving efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. Through implementing improvement strategies, allocating resources, and monitoring progress, organizations can embark on a successful continuous improvement journey, achieving sustainable growth and success in the long run.
What is Continuous Improvement?
Incremental improvement is an ongoing effort to enhance processes, products, and services. It involves a systematic approach to identify inefficiencies, eliminate waste, and make incremental changes to achieve better outcomes. This philosophy believes that every process can be improved and that small, continuous enhancements lead to significant improvements over time.
Benefits of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement offers numerous benefits to organizations of all sizes and across industries. By embracing this approach, businesses can:
- Enhance efficiency and productivity by streamlining processes and reducing waste.
- Improve product or service quality, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Foster innovation and creativity within the organization.
- Identify and seize opportunities for improvement.
- Cultivate a culture of learning and adaptability.
- Drive cost savings by eliminating unnecessary expenses.
- Stay ahead of the competition by continuously evolving and meeting customer expectations.
Continuous Improvement vs. Process Improvement
While continuous and process improvement are related concepts, they have distinct characteristics. Process improvement focuses on optimizing specific organizational processes, aiming to achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness. In contrast, continuous improvement takes a broader approach, encompassing all aspects of the organization’s operations, from processes to products and services. It emphasizes a culture of ongoing enhancement and encourages employees at all levels to contribute to improvement efforts.
Are you optimizing processes based on real-time data?
Manufacturing Operations Management Software (MOM) ensures visibility and control for ongoing refinement.
The Continuous Improvement Process
To effectively implement ongoing enhancement, organizations can adopt various methodologies and frameworks. Let’s explore two widely recognized approaches: the PDCA Cycle and Kaizen.
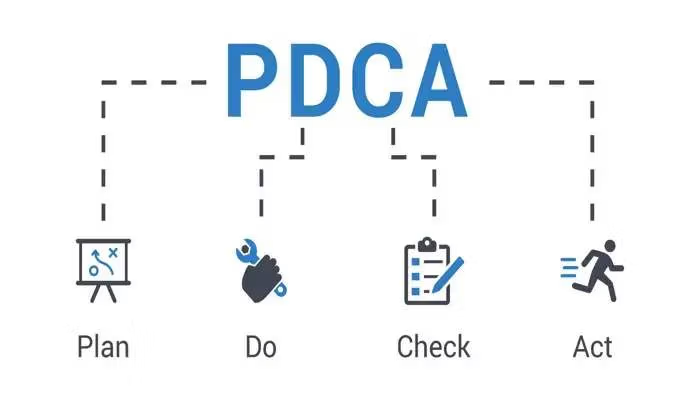
PDCA Cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act)
The PDCA cycle, also known as the Deming Cycle or the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, is a four-step iterative process that forms the cornerstone of continuous improvement. It consists of the following stages:
Plan: In this stage, organizations identify improvement opportunities, set goals, and develop plans to achieve them. This involves analyzing current processes, gathering data, and defining specific objectives.
Do: Once the plan is in place, organizations implement the proposed changes on a small scale or in a controlled environment. This allows them to assess the effectiveness of the changes and gather feedback.
Check: In this stage, organizations evaluate the results of the implemented changes. They collect and analyze data to determine whether the desired improvements have been achieved. If the results are satisfactory, the organization proceeds to the next step. Otherwise, they go back to the planning phase and make necessary adjustments.
Act: Based on the evaluation and analysis of the results, organizations take appropriate actions. They either standardize and implement the successful changes on a larger scale, refine the approach, and repeat the PDCA cycle to enhance the process further.
The Philosophy of Kaizen
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “Change for the better” or “Continuous Improvement,” is rooted in the Japanese culture and widely adopted by organizations worldwide. It emphasizes the involvement of all employees in the improvement process and encourages them to contribute their ideas and suggestions for enhancement.
Kaizen promotes a culture of continuous learning and incremental improvement. It recognizes that even gradual changes can lead to significant improvements over time. By fostering employee engagement and empowerment, organizations can tap into their workforce’s collective wisdom and creativity, driving continuous improvement.
Methodologies for Continuous Improvement
In addition to the PDCA cycle and Kaizen, several other methodologies can support organizations in their continuous improvement journey. Let’s explore a few of them:
Lean Methodology
Lean methodology, derived from the Toyota Production System, focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing value streams. It aims to deliver maximum value to customers while minimizing resources, time, and effort. Organizations can achieve greater efficiency and responsiveness by streamlining processes and removing non-value-added activities.
Kanban: Visualizing Workflow
Kanban, a visual management tool, enables organizations to visualize their workflow and manage tasks more effectively. It utilizes a Kanban board -a visual depiction of work items, status, and progress -to enhance transparency, collaboration, and efficient task management. By visualizing the workflow, organizations can identify bottlenecks, prioritize tasks, and ensure smooth workflow.
Value Stream Mapping: Identifying Improvement Opportunities
Value stream mapping is a technique used to analyze and improve the flow of materials, information, and activities within a process. It involves creating a visual representation of the current state and future state of the process, identifying areas of waste, and designing a more efficient and streamlined future state. Value stream mapping helps organizations identify improvement opportunities and optimize their processes.
Tools for Continuous Improvement
Organizations can leverage Organizations can leverage various tools that facilitate problem-solving, streamline workflows, and drive efficiency to implement a continuous improvement process. Let’s explore a few essential tools:
PDCA: A Four-Step Problem-Solving Approach
The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, as mentioned earlier, is a powerful tool for problem-solving and continuous improvement. Following the iterative PDCA process, organizations can systematically address issues, test solutions, evaluate outcomes, and make necessary adjustments. It provides a structured approach to problem-solving and ensures that improvements are based on data and evidence.
Kanban Board: Streamlining Workflows
A Kanban board is an effective visual tool for managing workflows and tasks. It allows organizations to visualize work items, track progress, and optimize the flow of work. By using a Kanban board, teams can collaborate more efficiently, identify bottlenecks, and ensure that work is completed promptly.
Process Automation: Enhancing Efficiency
Process automation involves using technology to automate repetitive and manual tasks. By automating routine processes, organizations can save time, reduce errors, and free employees to focus on more value-added activities. Process automation enhances efficiency and allows organizations to streamline their operations.
Total Quality Management: A Holistic Approach
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive approach to continuous improvement that focuses on delivering quality products and services. It involves engaging all employees in the pursuit of quality, implementing quality control measures, and continuously improving processes. TQM emphasizes customer satisfaction, employee involvement, and a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Implementing Continuous Improvement
Now that we have explored various methodologies and tools for continuous improvement, let’s discuss how organizations can effectively implement and sustain a culture of progressive development.
Creating a Culture of Incremental Improvement
To foster a culture of incremental improvement, organizations must prioritize and promote the value of ongoing enhancement. This involves:
- Communicating the importance of improvement to all employees.
- Encouraging and recognizing employee contributions and ideas.
- Providing training and development opportunities to enhance skills and knowledge.
- Establishing clear goals and metrics to measure improvement efforts.
- Celebrating successes and sharing best practices across the organization.
- Empowering employees to take ownership of improvement initiatives.
Employee Involvement and Engagement
Employee involvement and engagement are pivotal for successful continuous improvement. Organizations should actively involve employees at all levels, encouraging them to contribute their ideas, suggestions, and feedback. By creating a safe and supportive environment, organizations can harness their workforce’s collective intelligence and creativity, driving meaningful and sustainable continuous improvement.
Creating a Plan for Continuous Improvement
Organizations should develop a clear plan that outlines their goals, strategies, and actions to implement refinement effectively. Here are some steps to create a plan:
Assess Current State: Evaluate the current state of your organization’s processes, products, and services. Identify areas for improvement and prioritize them based on their impact and feasibility.
Set Goals: Define specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for improvement. These goals should align with the organization’s overall objectives and address the identified areas for enhancement.
Identify Strategies: Determine the strategies and approaches to help you achieve your improvement goals. Consider the methodologies and tools discussed earlier, such as PDCA, Kaizen, Lean, Kanban, and others relevant to your organization.
Allocate Resources: Allocate the necessary resources, including budget, time, and personnel, to support your improvement initiatives. Ensure that you have the essential tools, technologies, and training to facilitate the implementation of your strategies.
Implementation and Monitoring: Implement the planned initiatives and closely monitor their progress. Regularly collect and analyze data to assess the effectiveness of the implemented changes. Make adjustments as needed and ensure that you have mechanisms to track and measure the impact of your improvement efforts.
The Continuous Improvement Journey
Continuous improvement is an ongoing journey rather than a one-time project. Organizations that embrace this philosophy commit to a never-ending pursuit of excellence. Here are some aspects to consider:
Examples of Successful Initiatives
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented continuous improvement initiatives and achieved remarkable results. For example:
- Through its Toyota Production System, Toyota revolutionized the automotive industry by eliminating waste and continuously improving its processes.
- Amazon, known for its customer-centric approach, constantly seeks ways to enhance its delivery processes, customer experience, and operational efficiency.
- The healthcare industry has embraced continuous improvement to enhance patient care, reduce errors, and improve overall healthcare outcomes.
These examples demonstrate that organizations in various sectors can benefit greatly from improvement practices.
Measuring Success with Continuous Improvement
Measuring success in continuous improvement involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that reflect the organization’s improvement goals. These metrics can include:
- Efficiency metrics, such as cycle time, lead time, and throughput.
- Quality metrics include defect rates, customer complaints, and rework percentages.
- Cost metrics include cost savings, cost per unit, and return on investment (ROI).
- Customer satisfaction metrics include Net Promoter Score (NPS) or customer feedback ratings.
Regularly monitoring these metrics allows organizations to gauge the impact of their refinement initiatives and make data-driven decisions.
Overcoming Challenges in Continuous Improvement
Implementing incremental improvement can present challenges. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
Resistance to Change: Some employees may resist change due to fear or uncertainty. To address this, organizations should communicate the benefits of improvement, involve employees in the process, and provide training and support to help them adapt to changes.
Lack of Employee Engagement: Engage employees by creating a culture that values their input. Encourage and reward employee participation, provide platforms for sharing ideas, and recognize and celebrate employees’ contributions to refinement efforts.
Insufficient Resources: Limited resources, such as time, budget, or expertise, can hinder improvement initiatives. Organizations should prioritize improvement projects, allocate resources effectively, and seek creative solutions to overcome constraints.
Lack of Data and Measurement: Data is critical for assessing the effectiveness of improvement efforts. Organizations should establish data collection mechanisms, invest in data analysis capabilities, and define relevant metrics to measure improvement.
Sustainability: Iterative refinement requires long-term commitment and sustainability. Organizations should embed the culture of continuous improvement into their core values, provide ongoing training and support, and regularly review and refine improvement processes.
FAQ | Continuous Improvement
Why is continuous improvement essential for business success?
Continuous improvement, a key aspect of lean management methods, helps businesses enhance efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. It enables organizations to streamline processes, reduce waste, and identify and address inefficiencies. By continuously improving products, services, and operations, businesses can stay competitive, reduce costs, and drive sustainable growth.
How can companies build a strong culture of continuous improvement?
- Communicate the importance and benefits to all employees.
- Encourage and recognize employee contributions and ideas for improvement.
- Provide training and resources to empower employees to participate in improvement initiatives.
- Foster a safe and supportive environment where experimentation and learning from failures are encouraged.
- Incorporate continuous improvement principles into performance management and reward systems.
- Lead by example, with leaders actively participating in improvement efforts and demonstrating a commitment to continuous learning and growth.
What are some widely used tools for continuous improvement?
- PDCA cycle: Guides iterative problem-solving through planning, execution, evaluation, and adjustment.
- Kanban boards: Visualize workflow to manage tasks and limit bottlenecks.
- Value stream mapping: Identifies inefficiencies by mapping process flows.
- Process automation: Reduces manual effort and increases efficiency.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Focuses on continuous quality improvement across all operations.
What real benefits do businesses gain from continuous improvement?
- Increased productivity: Streamlines processes and eliminates inefficiencies.
- Enhanced quality: Reduces errors and ensures consistent standards.
- Reduced costs: Minimizes waste and optimizes resource use.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Delivers better products and services.
- Better employee engagement and morale: Encourages participation and ownership.
- Innovation: Fosters a culture of problem-solving and creativity.
- Sustainable growth: Ensures long-term competitiveness and adaptability.
- Agility and responsiveness: Helps organizations quickly adapt to market changes.
How can organizations successfully implement continuous improvement strategies?
Organizations implement continuous improvement initiatives by fostering a culture that encourages innovation, providing training and resources for employees, setting measurable goals, establishing feedback mechanisms, and integrating improvement processes into daily operations. Leadership support and commitment are also critical for successful implementation.
How does Six Sigma support continuous improvement?
Six Sigma enhances continuous improvement by reducing process variability and defects through data-driven analysis. It helps businesses identify inefficiencies, streamline operations, and improve quality, leading to more consistent and sustainable results.
What challenges do companies face when implementing continuous improvement?
- Resistance to change: Employees may hesitate due to uncertainty or added workload.
- Low engagement: Without clear communication, teams may not see the value.
- Limited resources: Time, budget, and expertise can be barriers.
- Sustaining momentum: Success requires long-term commitment and leadership support.
- Method selection: Choosing and integrating Lean or Six Sigma effectively can be complex.
- Change management: Without structure, improvements may not stick.
Image: Adobe Stock – Copyright: © Elnur – stock.adobe.com